Buy AutoTrafficRSS script now for $27 only!
We will send the script to your PayPal email within few hours,Please add FullContentRSS@gmail.com to your email contact.Source: Top 10 Off Page #SEO Techniques That Will Boost Your #Ranking
Buy AutoTrafficRSS script now for $27 only!
We will send the script to your PayPal email within few hours,Please add FullContentRSS@gmail.com to your email contact.
This article is part of an SEO series from WooRank. Thank you for supporting the partners who make SitePoint possible.
What is SEO?Search engine optimization is the collection of strategies, tactics and techniques used to rank highly in search engine results pages (SERPs) in order to increase the amount of traffic to a website. That's the traditional answer you'll find in featured snippets when you Google "what is SEO?" And it's not wrong — it's just a little incomplete.
The better, more accurate definition would be "the strategies, tactics and techniques used to rank highly in search engine results for the keywords used by your target audience in order to increase your conversions and reach."
Think of it this way: You own a pizza restaurant in your neighborhood, so you go about optimizing your site for pizza-related keywords. You do a really good job and now you rank in the top ten Google results for the keyword "pizza". The problem is, you're a local shop and your site isn't optimized for local search, so people looking for recipes, or the history of pizza, or the nutritional information of pizza are finding you, but maybe not people looking to order pizza in your neighborhood. This is a disaster because your customers aren't finding you when they are most likely to convert into a sale.
Making sure the right people find you at the right time is what SEO is really all about.
Do I Really Need to Do SEO?Yes.
Since you're reading about how to get started on SEO, you've probably already realized that you need it. But, if you're still on the fence, here are some numbers that should convince you:
So search optimization is really important in getting your audience onto your site. But there is another really important reason for you to be doing SEO: your competitors are doing it too. That means not only is our poor pizza restaurant missing out on current sales, its better-optimized competitors are forming relationships with customers, improving brand recognition and repeat sales.
How Do You Do SEO? Get Your Site Indexed by GoogleSince the goal of SEO is to rank highly in search results, your first step is to get your site crawled and indexed by Google. Submit your site to Google via Google Search Console, which doesn't require you to have an account. If you do have a Google Search Console account, use the Fetch as Google tool in the Crawl section. When Googlebot successfully fetches your page, click the "Submit to index" button.
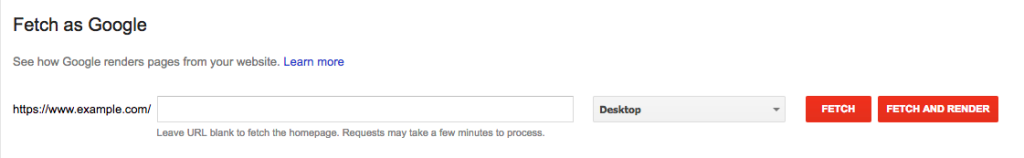
You can have Google index just the page you submitted by checking the box for URL, or have it index your whole site (assuming all of your pages can be reached by following your internal links), beginning with the submitted URL, by checking "URL and all linked pages".
You can submit your URL to Bing, which requires you to have a Bing Webmaster Tools account.
The next best way to get your site crawled by search engines is to get links to your site in as many (reputable) places as you can. Put a link to your website in the About section of your social media pages, particularly your Twitter profile. Make sure to link your website with your Google+ profile and set up a Google My Business account to link to your website. Not only will this increase your chance of getting your site crawled, it will help your chances of appearing in the Google Answer Box and optimize your knowledge graph rich snippet. If you've got a YouTube account for your business, add a link to your channel's About page and your video descriptions.
The vast majority of these links will be nofollow, so they won't actually help your ranking via improved link juice, but that's not the point here. Crawlers still follow those link and will index the sites they land on.
Finally, consider adding a blog to your site. People typically think of blogs as tools for content marketing and on page SEO, but they can also provide a steady stream of fresh content. Sites with blogs have an average of 434% more indexed pages than those without.
Find a more detailed look at getting crawled and indexed by Google here.
Keyword ResearchDespite rumors to the contrary, keywords are still very much relevant to SEO and picking the right keywords to optimize your site around is a core component of a successful SEO strategy. The process by which you find those keywords to target is called keyword research. Here are the basic steps to keyword research:
First, discover how people are currently finding you via search engines using Google Search Console, and which keywords are driving your best converting users via Google Analytics. If your site is really new, or doesn't get much organic traffic, get ideas from your products, categories or by answering the question "What is my website about?" or "What does my business do?" Find new keyword possibilities using a tool such as AdWord's Keyword Planner from Google or Bing's keyword research tool, among several other options.
Once you have a nice, long list of keywords you want to target, narrow it down to the those that have enough search volume to make them worth the effort. Google now prevents accounts that don't reach a certain, unspecified spend threshold, from accessing estimated search volume data, giving only a range of monthly searches. However, you can still access keyword volumes using WooRank's SERP Checker.

If you don't have a WooRank Pro or Premium account, you can use Bing's keyword research tool to find search volume. However, as Bing accounts for less than 10 percent of the market share of search, this data will only unlock the tip of the iceberg. Bing & Google's keyword tools use PPC data. It won't be 100% accurate, but it's close enough to draw accurate conclusions.
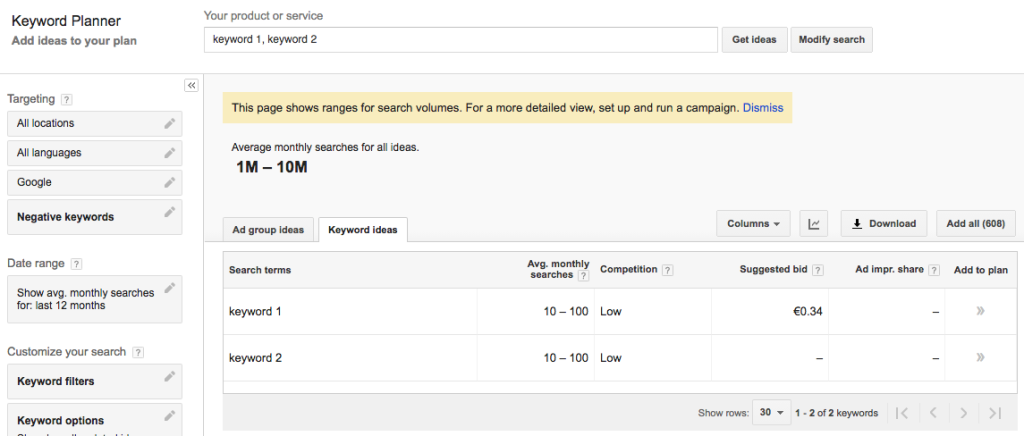
When finalizing your keyword strategy, make sure your portfolio has a nice mix of head and long tail keywords. Don't go overboard with either type. Head keywords will bring you lots of traffic, but it won't convert very well right away and there's a good chance you won't rank very well for them unless you're a rather big and well-established website. On the other hand, too many long tail keywords can convert like crazy, but won't bring in enough users to be viable.
Learn more about forming a keyword strategy and doing keyword research here.
Technical SEOKeywords are a core part of SEO, but there's more to it than that. You also need to build your site with search engines in mind. Here are the basic technical elements your site needs to improve its search engine optimization.
Robots.txtA robots.txt file is a simple text file in your website's root directory. It tells search engine bots which pages can and cannot be crawled. It's used mostly to keep search engines from indexing pages you don't want to show up in search results like temporary folders or your legacy site after a redesign or migration. You can block all user-agents, none or individual bots. A very basic robots.txt file that blocks all user-agents looks like this:
User-agent: * Disallow: /Allowing all robots to crawl your whole site looks like this:
User-agent: * Disallow:You can disallow specific user-agents from accessing specific folders, subfolders or pages by including them as disallow lines under the relevant user-agent line. Some search engines will recognize the 'allow' parameter so you can give access to specific files in disallowed folders.
Be very careful with your robots.txt file. Accidentally disallowing all bots, or certain user-agents to the entire server, is a relatively common, and easy-to-make, mistake that can cause huge headaches for SEOs. For an in-depth look at how to use robots.txt, check out our guide here.
XML SitemapsSitemaps are xml files that include every URL on a website and give a few basic details about each page. A simple sitemap for a website with just one page could look like this:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <urlset xmlns="http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9" xmlns:xhtml="http://www.w3.org/1999/html"> <url> <loc>https://www.example.com/</loc> <lastmod>2016-8-01</lastmod> <changefreq>monthly</changefreq> <priority>0.9</priority> <xhtml:link rel="alternate" hreflang="fr" href="https://www.example.com/fr/"/> </url>Here's a rundown of what that all means:
Your site will work and can get indexed without a sitemap, and they're not a ranking signal. But having a sitemap makes the whole process easier and faster. Plus, the more information you give about your pages, the more intelligently search engines can crawl your site, meaning bots are less likely to waste their crawl budget looking at unimportant pages. Sitemaps are especially important when you're adding new pages or launching a new site that doesn't have many links, or any links at all. For an in-depth look at XML sitemaps, check out this guide here.
Canonical URLsCanonical URLs help websites to prevent issues caused by duplicate content. They tell search engines where to find the original version of content that can be found at multiple URLs, showing them which one to list in the search results, and to combining link juice at a single URL.. There are all sorts of legitimate reasons you could end up with duplicate content: content management system, e-commerce product platforms and syndicated content. Search engines will see the rel="canonical" tag, know the content is a copy of the canonical URL, and pass on ranking information to the original page.
Rel="canonical" is implemented in the <head> of HTML pages and the HTTP header for non-HTML pages:
When you choose a canonical URL, pick the one that's best optimized for users and search engines, and has content that is well optimized. Make sure you've set a preferred domain in Google Search Console.
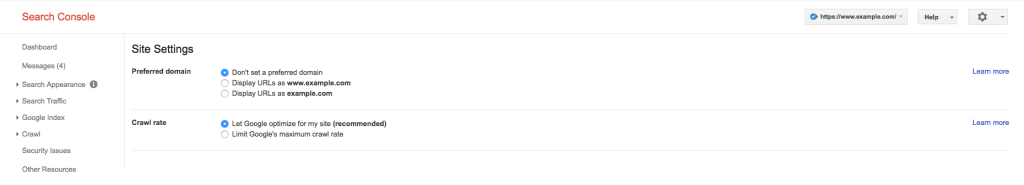
This works as a www resolve and Google will take this into account when it encounters links to your site out in the wild. It will pass link juice, trust and authority to your preferred domain, maybe with www, even when someone else uses a link without the www.
Learn more about rel="canonical" and dealing with duplicate content here.
URLsWriting URLs for both human and search engine usability is important — both have an impact on SEO. Use URLs to create a clear hierarchy of information so users always know where they are. Always use the canonical version of your URL (www resolve, https, etc.) and include folders, subfolders and the page, in that order.
URL structure is important to search engines because it helps them understand how that page relates to the rest of the site. Ideally the URL will be similar to your title tag, so it should include your keyword early on. Search engines look for keywords in URLs to determine the topic and relevance of a page.
Optimizing URLs will also help your backlink profile as people are more likely to use relevant anchor text for URLs that are well-structured and include keywords. This can help you to rank for these keywords. For a detailed look at optimizing URLs, check out this guide.
HTML Headers and Subheads<H1> – <H6> tags, also known as headers and subheads, denote the headlines and subheads on your page. These tags, especially the <H1> tag, are very important for SEO. Search engines use HTML headers to establish:
When using HTML header tags, there a couple of basic rules to follow. First, maintain the hierarchy of <H1> – <H6> tags. That means use the <H1> tag at the very beginning of the page, before any other, and then make sure more important headers have lower numbered tags. You don't want to bury section headers in an <H6> tag. Second, only use one <H1> tag per page. Since search engines rely so heavily on keywords in the header, using more than one could make it look like you're trying to manipulate your ranking. This is not good for SEO. (Note: You can use multiple <H1> tags as section headers if your pages uses HTML5. However, if it doesn't or you're not sure, stick to just one header.) And third, write your headers and subheads naturally. Search engines are pretty good at interpreting natural language, so over optimizing your HTML headers by keyword stuffing will hurt more than it helps.
For more information on using HTML headers for SEO and usability, read through this guide.
On Page SEOFinally, it's time to get into how best to optimize your pages to rank for your target keywords. On page SEO is probably the most well-known part, and is usually what people are thinking about when they talk about SEO. Here are the basic components to optimize on your pages.
Meta TagsThere are two meta tags in the HTML head of your page that are very important for SEO: title tags and meta descriptions. Title tags technically aren't meta tags, since they're not optional, but they're similar enough that they're included in the description.
Title tags, as you could probably guess, define the title of your page. They go in the <head> of the page like this:
<title>This is the Page Title</title>Search engines use these as a clue to determine what a page is talking about. In fact, they rely on title tags maybe more than any other on page factor, so they're really important. Optimize your title tags by:
Meta descriptions are a short explanation of your page's content. Use them to tell users what they should expect to get out of visiting your page. Search engines use this meta tag as part of a page's search snippet – the title, URL and description that's displayed in SERPs. When optimizing your meta descriptions be sure to:
In your page's code, the meta description looks like this:
<meta name="description" content="A short description of your page, 150-160 characters long, including spaces. Use this opportunity to encourage click throughs."/> Page ContentYour page content is the backbone of your SEO, both on page and off page (more on this later). When optimizing your page content, you need to use your keywords of course, but there's a lot more to it than that. Keep these principles in mind when writing your page content:
Get the most out of your content marketing by following our guide to creating evergreen content.
Image OptimizationSearch engines can't "see" images, but you can still use them to help your page rank for target keywords. This is done through the HTML alternative attribute (sometimes also called the alt tag or alt text). When you look at your page code, the alt attribute looks like this:
<img src="example-image.jpg" alt="Alt text describing the image"/>The alt attribute helps search engines determine if the image, as part of the page content, is relevant to a keyword. They are also used by screen readers to help the visually impaired, as well as showing up if an image fails to load. Use them to describe what's going on in your image, being as specific as you can. There's no real character count for alt text, but try to keep it to a half dozen words or so. Alt attributes will also help your images rank highly in image search results, which will open another channel for traffic acquisition.
For a more detailed look at optimizing your images, check out our guide.
LinksAfter you've optimized your page and content around your target keywords, you're ready to move on to links. Links are an important, maybe the most important, SEO signal. They essentially operate as a vote system for websites — each link is a little endorsement by someone that the linked page is valuable enough that their readers should check it out. These votes then pass on a little bit (or a lot, depending on the authority of the linking page) of value known as link juice. The more links a page has coming in, the more link juice it gets.
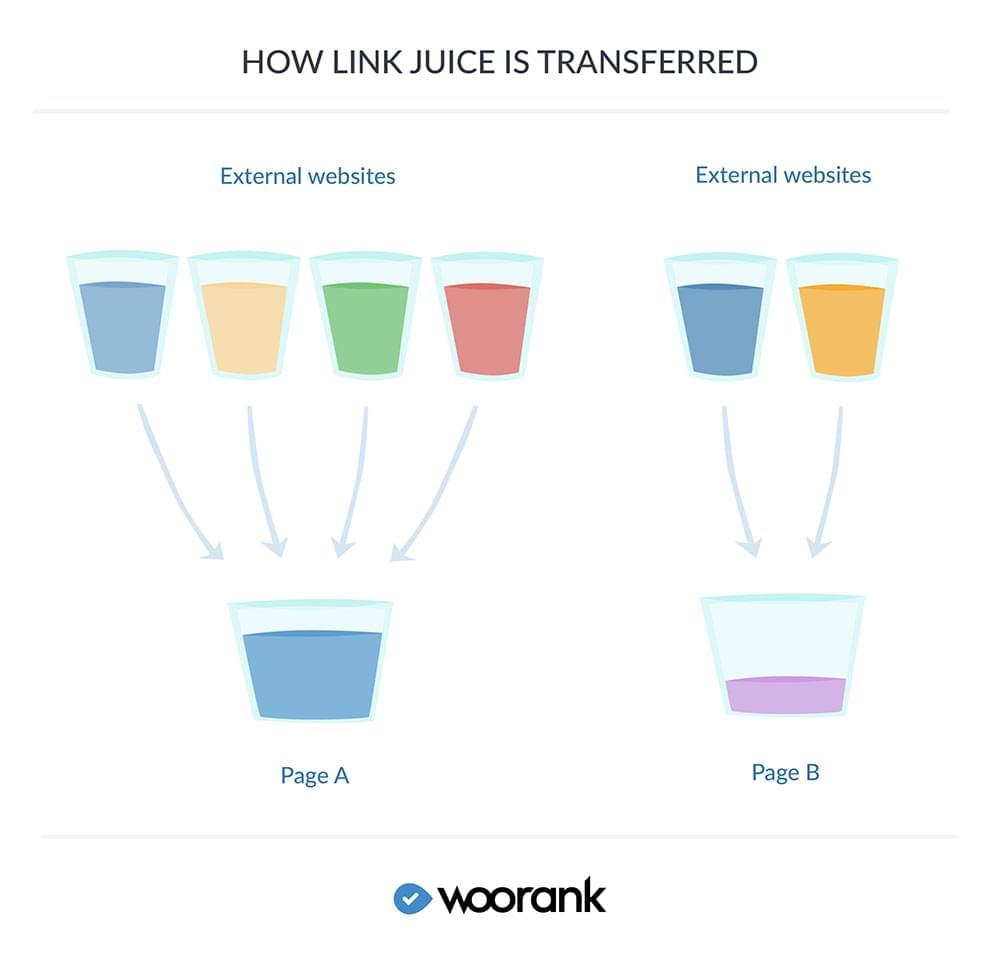
The nice thing about link juice is that you can spread it around your site via internal linking. Put links on pages that have lots of link juice, like your homepage, and point them at your important pages, like product or category pages. For more information on how to use links to improve your search ranking, check out this guide.
So what does this mean for your SEO? It means that building and maintaining a quality link profile is a major part of any search optimization campaign. There are three main components of any link building strategy:
It also means that you'll be conducting link audits fairly regularly. Since Google's Penguin 4.0 was incorporated into its core algorithm, you especially need to keep on top of your link profile to make sure you're only building quality links – Google now devalues low quality links so building these will only waste time. Google still issues manual link penalties, so if your link profile is made up of spammy links you may have some bad news coming. If you have a young site without a lot of links, you could also be at risk for negative SEO. It's pretty rare, but it does happen.
To get a detailed look at building links or conducting a link audit, read our guides here and here.
Wrapping It UpAs you can see, there's a lot going on when it comes to optimizing your pages for search engines. And this isn't even an in-depth look at everything you need to do to improve your search rankings to reach your audience online. However, if you follow the advice in this guide you'll be able to start improving your rankings and traffic quickly. If you want to take things to the next level, be sure to read the linked guides so you can really boost your website's performance in search results.
Buy AutoTrafficRSS script now for $27 only!
We will send the script to your PayPal email within few hours,Please add FullContentRSS@gmail.com to your email contact.Everything you need to know about SEO, delivered every Thursday.

Few marketing channels have evolved as quickly or as dramatically as search engine optimization (SEO). In its infancy, SEO was the shady practice of stuffing keywords, tweaking back-end code and spamming links until you started ranking well for the keywords you wanted. Thankfully, Google stamped out those practices pretty quickly, and its search algorithm has never really stopped evolving.
Much of Google's foundation was in place by the mid-2000s, but how has its algorithm — and as a result, our approach to SEO — changed in the past 10 years?
1. The rise of contentFirst, there's the rise of content marketing as part of a successful SEO strategy. Google has steadily refined what it considers to be "good" content over the years, but it was the Panda update in 2011 that served as the death blow to spammy content and keyword stuffing.
After Panda, it was virtually impossible to get away with any gimmicky content-based tactics, such as favoring a high quantity of content while forgoing quality and substance. Instead, the search engine winners were ones who produced the best, most valuable content, spawning the adoption of content marketing among SEOs — and content is still king today.
2. The death of link schemesGoogle has provided its own definition of what a "link scheme" actually is, along with some examples. Many find the guidelines here somewhat ambiguous, but the simplest explanation is this: Any attempt to deliberately influence your ranking with links could qualify as a scheme.
By the late 2000s, Google had worked hard to stamp out most black-hat and spam-based link-building practices, penalizing participants in link wheels and exchanges and paid linkers. But it was in 2012, with the Penguin update, that link building really became what it is today. Now, only natural link attraction and valuable link building with guest posts will earn you the authority you need to rank higher.
3. The reshaping of localCompared to 2006, local SEO today is a totally different animal. There have been dozens of small iterations and changes to the layout (such as the local carousel, and today's modern "3-pack" layout), but the biggest recent change to ranking factors was in 2014, with the Pigeon update.
With this update, Google more heavily incorporated traditional web ranking signals into its ranking algorithm, giving well-optimized websites a major edge in local search. Google also boosted the visibility of high-authority directory websites in its search results.
More generally, local searches have become more common — and more location-specific — over the last few years, thanks to mobile devices.
4. SERP overhaulsI can't tell you how many times the search engine results pages (SERPs) have changed, and not many people could; some of these changes are so small, it's debatable whether to even count them. But take a look at a SERP screen shot from 2006 and compare it to today, and you'll see how different your considerations must be.

Google search results in 2006. (Source)
5. The rise of the Knowledge GraphAnother major influencer in modern SEO has been Google's Knowledge Graph, which first emerged on the scene in 2012. The Knowledge Graph attempts to give users direct, concise answers to their queries, often presenting them with a box of information about a general subject or a succinct answer to a straightforward query. This is great for the user but often takes precedence over organic search results.
Accordingly, optimizers have had to compensate for this, either by avoiding generally answerable keyword targets altogether or by using Schema.org microformatting to make their on-site content more easily deliverable to the system.
6. Mobile prioritizationMobile devices have exploded in popularity since the iPhone first emerged back in 2007, and Google has done everything it can to emphasize the importance of optimizing websites for those mobile users. Indeed, in 2015, mobile queries officially surpassed desktop queries in Google search.
Optimizing for mobile has become not only common, but downright required these days, in no small part due to Google's continuing and escalating insistence. Its mobile-friendly update, which occurred in two separate phases, has been a major enforcer of this new standard.
7. The soft death of keywordsPanda and Penguin killed off the practice of keyword stuffing, but a smaller, more curious update in 2013 spelled the "soft" death of keyword optimization altogether. Hummingbird is the name of the update that introduced semantic search, Google's way of deciphering user intent rather than mapping out individual keywords and phrases.
Today, Google attempts to understand meaning rather than matching keywords, so keyword-centric optimization doesn't work the same way. However, keyword research is still relevant, as it can help guide your strategic focus and provide you with ranking opportunities.
8. Update pacing and impactIt's also worth noting that for a time — in the few years following Panda — Google stressed out search optimizers by releasing seemingly random, major updates to its search algorithm that fundamentally changed how rankings were calculated. However, now that the search engine has reached a strong foundation, the significance and pacing of these updates have declined. Today, updates are smaller, less noticeable, and roll out gradually, giving them a much less dramatic impact on the industry.
Final thoughtsUnderstanding where SEO has come from and where SEO stands today will help you become a better online marketer. Hopefully, by now you've long ago eliminated any black-hat techniques in your strategy.
Google — and we, as marketers alongside it — are constantly pushing this now-fundamental element of our lives forward, so if you want to stay relevant, you'll need to keep focused on the next 10 years of search engine updates.
Some opinions expressed in this article may be those of a guest author and not necessarily Search Engine Land. Staff authors are listed here.
About The Author Jayson DeMers is the founder & CEO of AudienceBloom, a Seattle-based content marketing & social media agency.Buy AutoTrafficRSS script now for $27 only!
We will send the script to your PayPal email within few hours,Please add FullContentRSS@gmail.com to your email contact.
Getting your school found online is an ongoing battle that requires different strategies for different goals. Search engine marketing (SEM) is comprised of both search engine optimization (SEO) and pay-per-click (PPC) campaigns. You can use both these strategies to direct traffic to your school's website, blog, or other digital assets you have, e.g. a landing page/microsite promoting a new school program.
While both strategies can drive traffic, they have different virtues. To maximize your spend and get the best return, you want to use the right strategy for the right reasons.
Where SEO and PPC DifferSEO is about building a strong content foundation that earns you more attention as time goes on. It's a long-term investment that has a lower cost with slower rate of return. Yet there comes a tipping point at which your SEO-optimized digital assets provide exponential returns. Its value doesn't reside in only a few specific high performing pages — the collective value starts boosting newer content as well. The more authority your site builds over time, that authority applies to other content you post on your site. Your SEO-optimized pages create a perpetual flow of traffic.
Infusing all your digital assets with SEO best practices should be part of your standard practice for every piece of digital content your school publishes.
You can download our full ebook on SEO for schools here >>In contrast, a PPC campaign is fixed-time campaign that will have high upfront costs, but can get you quick, valuable returns. Your PPC campaign will be designed around a keyword strategy, just like your SEO. Unlike SEO, the PPC campaign only brings in returns for the time you're paying for the ad space. There's no long term benefit or exponential growth. That doesn't mean PPC doesn't have its role to play in getting your school found. It just means you want to pick your spots.
How and When to Use SEOReally, the answer to "when" is "always." As mentioned earlier, SEO is the foundation that will push your website and blog higher and higher in the search engine results page (SERP). Virtually all searchers click on a first page link in their search results rather than a PPC ad.
Of course, getting ranked for "culinary school" isn't going to be easy (it's a very competitive term). And the truth is, you don't want to. That's far too broad a keyword. Your SEO strategy will return the most relevant visitors to you if work with long tail keywords (LTKs) that are queries containing the language your ideal students use to search for what they want. So if you're a school with a culinary management program that offers an online learning component, you might find "online culinary management degree program" more effective.
The more relevant your long tail keywords are to your personas, the more interested and qualified an audience you'll attract.
After researching and identifying the most relevant collection of long tail keywords, you need to execute your SEO strategy through on-page and off-page optimization.
On-page SEOThis where you have the most control. On-page SEO uses all the smart ways to embed a page's keyword throughout the page. This doesn't mean repeating the keyword over and over in your text. Those days are long gone. Instead, you'll use the keyword a few times in your text. You'll write naturally as Google also looks for the phrases it expects to see if your program page is truly about an "online culinary management program." So Google might also expect to see other culinary related phrases such "back of the house" or "restaurant operations."
You also have a variety of tags (i.e. title tags, meta tags, heading tags, and descriptions), where you can use your selected keywords. Some of these tags (e.g. your URL, title tag, and meta description) appear in the search results, so are critical to getting the click. Other tags, (e.g. alt-text tags — used to optimize images), don't always get seen by visitors. But the search engine bots deciding where to rank your page see and use them. Your title tag is probably the most important tag in terms of SEO, but don't overlook any of them.
Google has recently changed a number of its properties for on-page tags, such as giving you more room in titles and descriptions. When these changes happen, it's a good time to give your pages an SEO refresh.
Other on-page tactics to remember are: give the page a quick loading time and incorporate your social sharing buttons so visitors can spread your awesome content.
Off-page SEOOff-page SEO is when high authority sites link back to your awesome content. You have no control over this, because it requires external sites to like your content and link to it. However, you can encourage this process by sending a lot of social sharing signals in your content.
You want social sharing icons on all your pages, posts, and emails. And you can do more. You can craft copy to encourage people to share by reminding them to do so. You can also create pre-fabbed Tweets and Shares in your content for them to use.
Let's say you have a blog post of interviews with well-known restaurateurs sharing what personal and technical skills they look for when hiring a restaurant manager. Using the "birds of a feather" principle, you might add some copy to above your social sharing icons that says, "Know someone who's wondering if they have what it takes? Help them find out. Share this article." Or "Tweet this: Graduate as a #Chef from this #Top-Ranked #CulinaryProgram @[YourSchoolTwitterHandle] [url]."
The more your blogs posts and web pages get out there, the more likely people will start to link back to them.
How and When to Use PPCWhile SEO is strategic and on-going, PPC is more tactical. PPC ads are those ads you see at the top of your search results. Since a PPC campaign only runs as long as you're willing to pay for it, you want to reserve for when you have something very specific you want to promote.
Sticking with our culinary management program example, if this is a new program and you want to drive awareness as well as attract immediate potential students, a PPC program could be a good choice here.
Another good use case for PPC is to support a specific enrollment priority. Perhaps your school wants to attract students with high musical ability to improve your band and orchestra. Your team has invested a lot of resources creating a report on how music education improves overall learning, which can help students in their future college admissions. You set up a detailed workflow, filled with smart lists and triggered email series to nurture the leads who download this report. Building a PPC campaign around promoting this report could be a valid expense to make this a wide funnel entrance point into your database.
A third place for a PPC campaign may be in growing your funnel numbers for the upcoming year when they're a bit low. If you need a boost in prospects to get the right number of school applicants, a PPC campaign may help. Keep in mind that in this case, you're not looking for people in the attraction stage (top-of-the-funnel). They will more likely already be in their consideration stage (middle-of-the-funnel). So select your promoted keywords and content appropriately.
Use this PPC ad calculator to find out if using a PPC campaign makes economic sense for a specific campaign.
In short: think of SEO as your "always-on" SEM, while PPC is your "special occasion" SEM. You need both, but in the right proportion and places.

Buy AutoTrafficRSS script now for $27 only!
We will send the script to your PayPal email within few hours,Please add FullContentRSS@gmail.com to your email contact.